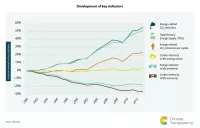
Since the 2015 adoption of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals and the success of the Paris Agreement under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), it has become clear that “business as usual” is no longer an option for neither industrialized countries nor the developing world. Both the Agenda 2030 and the Paris Agreement (PA) entail substantial consequences for the world financial system. Mobilizing the massive investment required for climate resilient, low-carbon infrastructure and development, transforming the world economy and hedging the climate-related risk to the financial system form formidable challenges to the public and the private sector alike.